Appearance
MyBatis教程 - 8 多对一和一对多
在实际开发中,一对多和多对一是经常遇到的,比如用户和订单,一个用户会有多个订单,这个就是一对多;多对一就是反过来,多个订单对应一个用户。
我们这里以班级和学生为例,一个班级会有很多的学生,一对多;多个学生属于一个班级,多对一。
表关系如下:

这里为了避免和 Java 中的 class 关键字冲突,使用 cla55。
这里的多对一和一对多解决什么问题呢?
多对一的时候,每个学生都有对应的班级,查询学生信息的时候,会将班级的 ID 查询出来,能否创建学生实例,其中包含 Cla55 班级信息,查询学生信息,直接将班级的信息也查询出来,而不仅仅是班级ID。
学生类,Student.java :
java
public class Student {
private Integer id;
// 班级的对象信息
private Cla55 cla55;
private String name;
private Integer age;
}就像上面的学生类,查询学生信息的时候,将班级的信息查询出来,存储在 Cla55 对象属性中。
同样,一对多的时候,每个班级会有很多的学生,查询班级信息的时候,能否将班级中所有的学生信息也查询出来,放到 List 属性中,如下:
班级类,Classes.java
java
public class Cla55 {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer studentCount;
// 学生信息
private List<Student> studentList;
}这就是多对一和一对多要解决的问题。
8.1 准备工作
首先创建两张表,并添加一些数据:
sql
-- 班级表
CREATE TABLE tb_cla55 (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT NULL,
`student_count` INT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
-- 插入班级数据
INSERT INTO tb_cla55 (id, name, student_count)
VALUES
(1, '一年一班', 38),
(2, '二年二班', 45),
(3, '三年三班', 43);
-- 学生表
CREATE TABLE tb_student (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`cla55_id` INT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` INT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
-- 插入学生数据
INSERT INTO tb_student (id, cla55_id, name, age)
VALUES
(1, 1, '张三', 12),
(2, 1, '李四', 13),
(3, 2, '王五', 13),
(4, 3, '赵六', 14),
(5, 4, '钱七', 15);8.1多对一
多对一,多个学生对应一个版本,所以每个学生是有一个班级信息的。所以在学生表添加班级对象信息。
Student.java
java
package com.foooor.mybatis.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Student {
private Integer id;
// 班级的对象信息
private Cla55 cla55;
private String name;
private Integer age;
}Cla55.java
java
package com.foooor.mybatis.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.List;
@Data
public class Cla55 {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer studentCount;
}因为这里处理的是多对一,所以先去掉 Cla55 类中的 studentList。
如果单纯的使用 SQL 查询学生信息和对应的班级信息,SQL 应该是这样的:
sql
-- 查询ID为1的学生的信息和班级信息
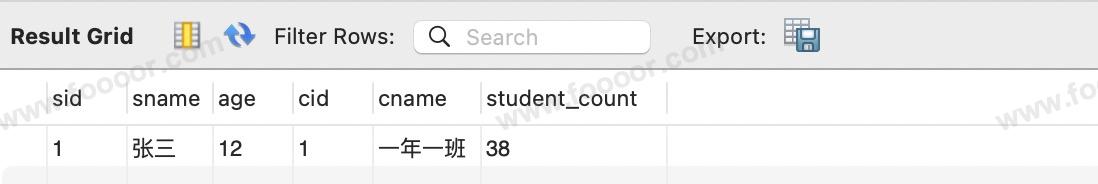
SELECT stu.id as sid, stu.name as sname, stu.age, cla.id as cid, cla.name as cname, cla.student_count
FROM tb_student as stu LEFT JOIN tb_cla55 as cla ON stu.cla55_id = cla.id
WHERE stu.id = 1;可以使用左连接、内连接、右连接都可以,为了避免两张表字段重名,查询使用了别名。
SQL 查询结果如下:
下面介绍三种方式实现多对一。
8.1.1 使用级联属性赋值
首先创建 StudentMapper.java,在其中定义接口如下:
java
/**
* 根据id查询学生信息
*/
Student selectStuAndClassById(@Param("id") Integer id);没有什么特别。
然后创建 StudentMapper.xml,在其中定义 ResultMap 和 SQL 映射方法:
xml
<resultMap id="StudentMapResult" type="Student">
<id property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<result property="age" column="age"/>
<result property="cla55.id" column="cid"/>
<result property="cla55.name" column="cname"/>
<result property="cla55.studentCount" column="student_count"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- 根据Id查询学生和班级信息 -->
<select id="selectStuAndClassById" resultMap="StudentMapResult">
SELECT stu.id as sid, stu.name as sname, stu.age, cla.id as cid, cla.name as cname, cla.student_count
FROM tb_student as stu LEFT JOIN tb_cla55 as cla ON stu.cla55_id = cla.id
WHERE stu.id = #{id};
</select>在上面的代码中,使用 ResultMap 与查询结果进行映射(与查询结果字段名称映射),并通过 Student 类中的 cla55 属性进行级联映射。
编写测试方法,没什么特别的:
java
@Test
public void testSelectStudentById() {
// 获取SqlSession连接
SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Integer sid = 1;
// 查询用户列表
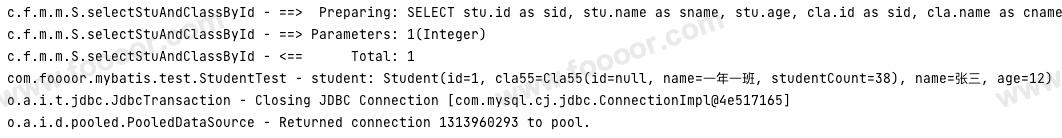
Student student = studentMapper.selectStuAndClassById(sid);
log.info("student: {}", student);
// 关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}执行结果如下,打印的学生信息中包含了班级信息:
8.1.2 使用association
修改 ResultMap 即可,使用 <association> 标签进行关联 cla55 对象属性的映射:
xml
<resultMap id="StudentMapResult" type="Student">
<id property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<result property="age" column="age"/>
<association property="cla55" javaType="Cla55">
<id property="id" column="cid"/>
<result property="name" column="cname"/>
<result property="studentCount" column="student_count"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<!-- 查询方法不用变 -->
<select id="selectStuAndClassById" resultMap="StudentMapResult">
SELECT stu.id as sid, stu.name as sname, stu.age, cla.id as cid, cla.name as cname, cla.student_count
FROM tb_student as stu LEFT JOIN tb_cla55 as cla ON stu.cla55_id = cla.id
WHERE stu.id = #{id};
</select><association>专门用来处理多对一映射关系的,property对应的是属性名,javaType对应的是 Cla55 的类型。
效果和上面使用级联属性赋值是一样的。
8.1.3 分步骤实现多对一
上面实现多对一,都是一次性将数据全部查出来,然后进行数据的映射。
我们还可以使用多个步骤来实现,也就是先查出学生信息,然后再根据学生信息中的班级 ID 去查询班级信息。
1 分步骤实现
首先实现 StudentMapper.java 中的接口,用来查询学生信息:
java
/**
* 根据id查询学生和班级信息
*/
Student selectStuAndClassById(@Param("id") Integer id);没什么特别的。
然后编写 StudentMapper.xml :
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.foooor.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper">
<resultMap id="StudentMapResult" type="Student">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<result property="age" column="age"/>
<association property="cla55" select="com.foooor.mybatis.mapper.Cla55Mapper.selectById" column="cla55_id"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- 根据Id查询学生和班级信息 -->
<select id="selectStuAndClassById" resultMap="StudentMapResult">
SELECT * FROM tb_student
WHERE id = #{id};
</select>
</mapper>- 首先查询学生的 SQL 映射没什么特别的,就是单纯的查询学生,但是结果集使用
ResultMap,重点在ResultMap的定义。 ResultMap中,前面还是学生字段的基本映射,没有什么特别,不同的是后面的<association>标签。property="cla55"对应的是 Student 类中的cla55属性,column="cla55_id"表示的是以查询学生结果中的cla55_id字段为参数,调用com.foooor.mybatis.mapper.Cla55Mapper(要全类名)中的selectById方法。
所以现在还需要创建 Cla55Mapper 的 selectById 方法,用来查询班级信息:
Cla55Mapper.java :
java
/**
* 根据id查询
*/
Cla55 selectById(@Param("id") Integer id);Cla55Mapper.xml :
xml
<select id="selectById" resultType="Cla55">
SELECT * FROM tb_cla55
WHERE id = #{id}
</select>这个没什么特别的,就是普通的查询。
通过上面的实现,查询分为两个步骤,一个是查询学生,根据查询出的学生的班级 ID,继续查询班级信息。
执行测试方法,发现执行了两条 SQL ,如下:
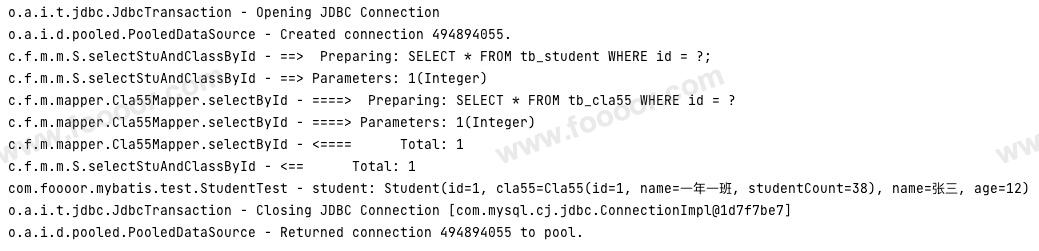
为什么要这样实现呢,有什么好处呢,感觉前两种实现方式挺好的,这种反而有种脱裤子放屁的感觉?
分步查询的优点是可以实现延迟加载(懒加载),当获取学生信息的时候,会查询学生信息,暂时不会查询班级信息,当去获取班级信息的时候,才去查询班级信息。
2 全局延迟加载
延迟加载默认是关闭的,需要在 mybatis-config.xml 全局配置文件中配置开启:
xml
<!-- 全局设置 -->
<settings>
<!-- 驼峰命名法 -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
<!-- 懒加载,当开启时,所有关联对象都会延迟加载。 -->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>开启懒加载后,通过下面的代码测试:
java
@Test
public void testSelectStudentById() {
// 获取SqlSession连接
SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Integer sid = 1;
// 查询用户列表
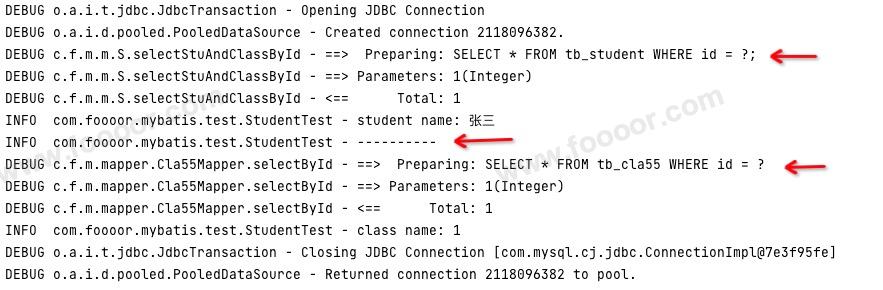
Student student = studentMapper.selectStuAndClassById(sid);
log.info("student name: {}", student.getName());
log.info("----------");
log.info("class name: {}", student.getCla55().getName());
// 关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}通过执行结果可以发现,当执行 student.getCla55().getName() 的时候,才会获取班级信息。
3 局部延迟加载
上面配置的延迟加载是全局生效的,如果想要只针对某个 ResultMap 生效,可以在 ResultMap 的 <association> 标签中进行配置:
xml
<resultMap id="StudentMapResult" type="Student">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<association property="cla55"
select="com.foooor.mybatis.mapper.Cla55Mapper.selectById"
column="cla55_id"
fetchType="lazy" />
</resultMap>fetchType="lazy" 表示使用延迟加载,还可以配置为 fetchType="eager" 表示立即加载。
8.2 一对多
下面来介绍一对多。
一对多,每个班级都有对应的学生列表信息,所以班级类中有一个学生列表的属性。
Class55.java
java
package com.foooor.mybatis.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.List;
@Data
public class Cla55 {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer studentCount;
// 学生信息
private List<Student> studentList;
}Student.java
java
package com.foooor.mybatis.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
}一般要么是一对多查询,要么是多对一查询,所以不可能是查询 Cla55 的时候,获取到学生的列表,然后学生列表中每个学生的对象中又包含了班级的信息,形参循环,所以这里我将 Student 对象中的 Cla55 班级属性给去掉了。
下面介绍两种实现一对多的方式。
8.2.1 使用collection
如果单纯的使用 SQL 查询班级信息和对应的学生信息,SQL 应该是这样的:
sql
-- 查询ID为1的班级信息和学生信息
SELECT cla.id as cid, cla.name as cname, cla.student_count, stu.id as sid, stu.name as sname, stu.age
FROM tb_cla55 as cla LEFT JOIN tb_student as stu ON cla.id = stu.cla55_id
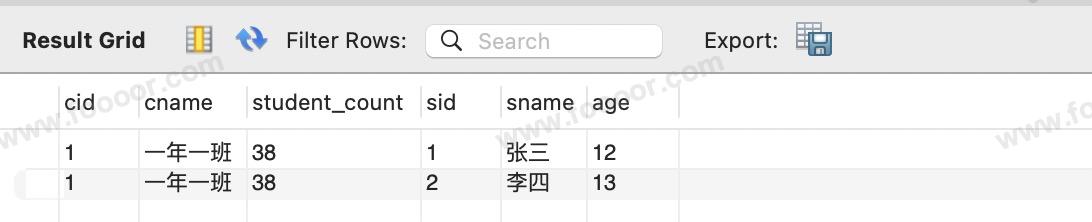
WHERE cla.id = 1;可以使用左连接、内连接、右连接都可以,为了避免两张表字段重名,查询使用了别名。
SQL 查询结果如下:
首先创建 Cla55Mapper.java,在其中定义接口如下:
java
/**
* 根据id查询班级和学生信息
*/
Cla55 selectClassAndStuById(@Param("id") Integer id);没有什么特别。
然后创建 Cla55Mapper.java,在其中定义 ResultMap 和 SQL 映射方法:
xml
<resultMap id="Cla55ResultMap" type="Cla55">
<id property="id" column="cid"/>
<result property="name" column="cname"/>
<result property="studentCount" column="student_count"/>
<!--
property:表示集合属性的名称
ofType:表示集合属性的类型
-->
<collection property="studentList" ofType="Student">
<id property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<result property="age" column="age"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectClassAndStuById" resultMap="Cla55ResultMap">
SELECT cla.id as cid, cla.name as cname, cla.student_count, stu.id as sid, stu.name as sname, stu.age
FROM tb_cla55 as cla LEFT JOIN tb_student as stu ON cla.id = stu.cla55_id
WHERE cla.id = #{id};
</select>SQL 使用的是上面查询的SQL,主要是 ResultMap 中使用 <collection> 标签与 Class5 类中的 List<Student> 属性进行映射,需要指定 property 和 ofType , ofType 为集合中的数据类型。
编写测试代码:
java
@Test
public void testSelectStudentById() {
// 获取SqlSession连接
SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSession();
Cla55Mapper cla55Mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(Cla55Mapper.class);
Integer cid = 1;
// 查询用户列表
Cla55 cla55 = cla55Mapper.selectClassAndStuById(cid);
log.info("cla55 {}", cla55);
// 关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
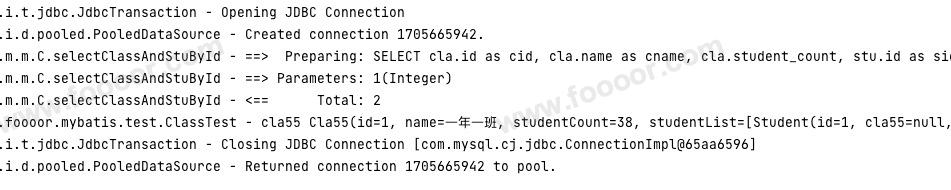
}执行结果如下,虽然上面单独执行 SQL 查询的是多条记录,但是 Cla55 信息是一样的,可以映射为一条 Cla55 对象:
8.2.2 分步实现一对多
同样,一对多也可以使用分步查询,并实现懒加载。
分步查询首先是查询班级信息,然后根据班级的 ID 来查询学生的信息。
首先在 Cla55Mapper.java 中定义接口,查询班级信息,如下:
java
/**
* 根据id查询班级和学生信息
*/
Cla55 selectClassAndStuById(@Param("id") Integer id);没有什么特别。
然后编写 Cla55Mapper.xml :
xml
<resultMap id="Cla55ResultMap" type="Cla55">
<id property="id" column="cid"/>
<result property="name" column="cname"/>
<result property="studentCount" column="student_count"/>
<!--
studentList:Cla55类中的集合属性
select:表示要执行查询学生信息的方法
id:首先查询的是班级的信息,返回的是id,然后根据这个id去查询学生,所以这里的id为班级的id
-->
<collection property="studentList"
select="com.foooor.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper.selectByCla55Id"
column="id">
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectClassAndStuById" resultMap="Cla55ResultMap">
SELECT * FROM tb_cla55
WHERE id = #{id}
</select>ResultMap 还是使用 <collection> 标签来映射,不过要指定 select 表示查询学生信息要使用的方法。
这里的 column="id" 表示的是班级的 id,传递给 StudentMapper.selectByCla55Id ,表示根据班级 id 查询学生。
所以现在还需要创建 StudentMapper 的 selectById 方法,用来查询学生信息:
StudentMapper.java :
java
/**
* 根据班级id查询学生信息
*/
List<Student> selectByCla55Id(@Param("cla55Id") Integer cla55Id);StudentMapper.xml :
xml
<!-- 根据班级Id查询学生信息 -->
<select id="selectByCla55Id" resultType="Student">
SELECT * FROM tb_student
WHERE cla55_id = #{cla55Id};
</select>这个没什么特别的,就是普通的查询,但是返回的结果是集合,因为根据班级 ID 查询出的是一个学生的集合。
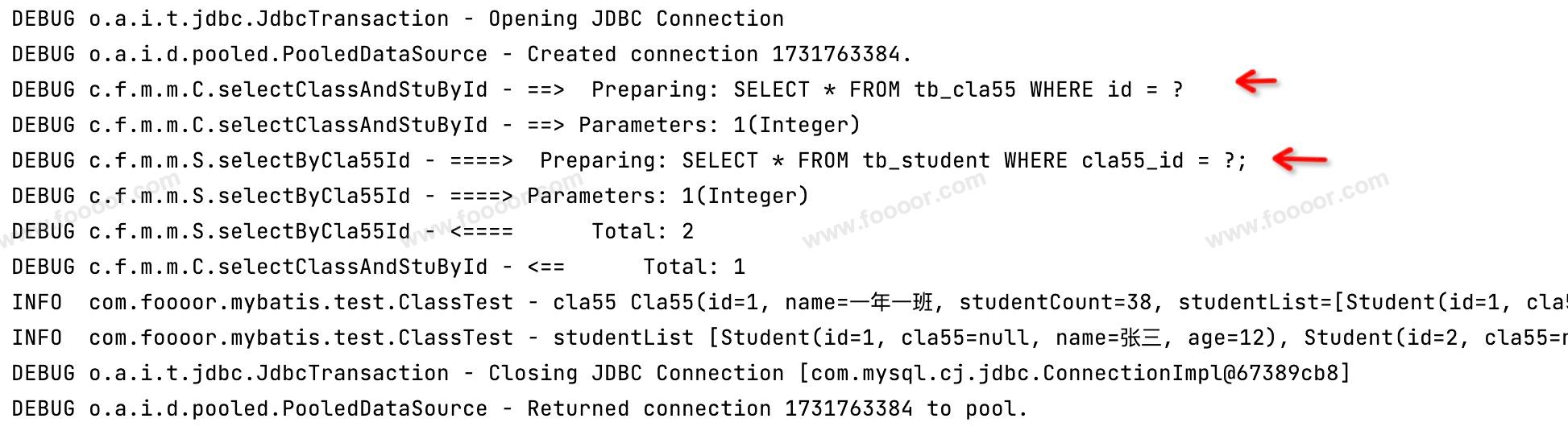
通过上面的实现,查询分为两个步骤,一个是查询班级,根据查询出的班级 ID,继续查询学生信息。
执行测试方法,发现执行了两条 SQL(没有配置延迟加载) ,如下:
8.2.3 配置延迟加载
和多对一的延迟加载的配置方法是一样的。
1 全局配置
在 mybatis-config.xml 中配置:
xml
<!-- 设置 -->
<settings>
<!-- 驼峰命名法 -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
<!-- 懒加载,当开启时,所有关联对象都会延迟加载。 -->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>2 局部配置
在 ResultMap 中配置:
xml
<resultMap id="Cla55ResultMap" type="Cla55">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<result property="studentCount" column="student_count"/>
<!--
fetchType的值:
eager: 表示立即加载
lazy: 表示延迟加载
-->
<collection property="studentList"
select="com.foooor.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper.selectByCla55Id"
column="id"
fetchType="eager">
</collection>
</resultMap>